ultrasound
Ultrasound
When it comes to medical imaging, ultrasound is one of the most versatile and widely used technologies available. It's non-invasive, painless, and can provide doctors with a wealth of information about the body's internal structures, making it an indispensable tool for diagnosing a wide range of conditions.
If you're in Kenya and in need of an ultrasound, you're in luck. LifeCare Hospitals, a leading healthcare provider in the country, has established ultrasound test centres in Bungoma, Kikuyu, Meru, Migori, and Eldoret, bringing advanced medical imaging technology closer to patients than ever before.
How Ultrasound Works?
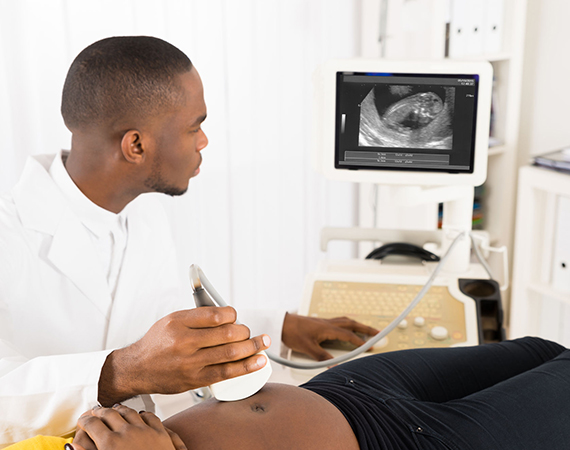
Ultrasound works by sending high-frequency sound waves into the body. These sound waves bounce off the body's internal structures and are then detected by a transducer, a small handheld device that's placed on the skin.
The transducer sends the sound waves to a computer, which processes them into images that can be viewed on a screen. The images can be 2D, 3D, or even 4D, depending on the type of ultrasound being performed.
Ultrasound is a very safe and painless procedure. Patients may be asked to change into a hospital gown and lie down on a table. A clear gel is applied to the skin to help the transducer make good contact with the body. The technologist will then move the transducer over the area being examined, capturing images from different angles as needed.

Limits and risks of ultrasound
Ultrasound is a harmless procedure and does not produce radiation as x-rays. Still, ultrasound has some biological effects on the body under specific settings and conditions. Ultrasound has limits. Sound waves cannot travel well through air and bones. So ultrasound cannot image the body parts hidden through bone or filled with gas. For in-depth imaging, consultants often suggest other imaging techniques like MRI.
The Benefits of Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a safe and painless way to get detailed images of the body's internal structures. Unlike X-rays, which use ionizing radiation, ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of organs, tissues, and other structures.
One of the main benefits of ultrasound is that it's non-invasive. There are no needles or probes involved, so there's no risk of infection or other complications. Ultrasound is also painless and generally well-tolerated, making it a good option for patients of all ages.
Ultrasound is also highly versatile. It can be used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, including:
- Pregnancy: Ultrasound is perhaps best known for its use in obstetrics. It can be used to monitor fetal growth, check for abnormalities, and even determine the baby's sex.
- Abdominal conditions: Ultrasound can be used to evaluate the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and other abdominal organs. It can help diagnose conditions such as gallstones, liver disease, and pancreatitis.
- Cardiac conditions: Ultrasound can be used to evaluate the structure and function of the heart. It can help diagnose conditions such as heart valve disease, congenital heart defects, and heart failure
- Musculoskeletal conditions: Ultrasound can be used to evaluate soft tissue injuries such as sprains, strains, and tears. It can also be used to diagnose conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome and tennis elbow.
- Ultrasound can also be used to diagnose conditions such as thyroid disease, kidney stones, and certain types of cancer.
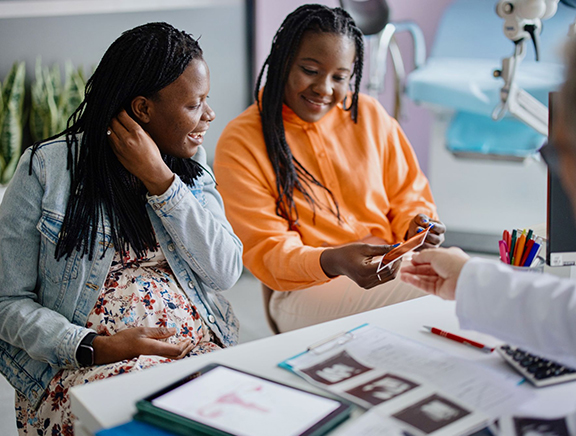

During an ultrasound, a water-based gel is applied on the surface to ensure no air pockets are between the skin and the transducer. The device sends ultrasound signals inside to body to create an image.
Sometimes, an ultrasound gets done inside your body. In this case, the probe gets inserted inside the body through our natural openings. Some examples of internal ultrasound are
- Transesophageal echocardiogram: The transducer is inserted into the esophagus to obtain heart images. The patient gets sedated during this procedure.
- Transrectal ultrasound: It is to test the prostate by inserting the transducer inside the rectum
- Transvaginal ultrasound: A transducer is inserted into the vagina to check the uterus and ovaries.
FAQs
Do you have any Questions? We are here!

Yes, ultrasound is a very safe and non-invasive procedure.
Depending on the type of ultrasound being performed, you may be asked to avoid eating or drinking for a certain period of time before the test. Your doctor will provide you with specific instructions.
No, ultrasound is generally painless and well-tolerated.
The length of the test will depend on the type of ultrasound being performed and the area of the body being evaluated. Most tests take between 30 and 60 minutes.
Why choose us?
Safe Care: Delivering health care which minimizes risks and harm to service users.
Reliable Care: Ability to successfully provide safe and person-centered care repeatedly. That we are effective, efficient and accessible/timely.
Patient Experience: Patients are an integral part of experiencing quality and safety related processes and are the ultimate recipients of care and judges of quality. That we are equitable and patient-centered in service delivery.
